
What is Bioaccumulation?
What do you get when you decompose the term "bioaccumulation"? The word accumulation meansSomethingThe accumulation of, and the prefix bio- meanlife. Put it together, it is.Something accumulates in living things.To defineBioaccumulation.
Then biological accumulation is used to refer toChemical substances in organismsThe accumulation of. These substancesCann’t be metabolized , it accumulates in organisms and accumulates through the food habits of consumers at all levels in the food chain.The higher the level, the higher the cumulative concentration in the body of consumers.The phenomenon.
How does bioaccumulation occur?
One way is to let a certain amount of chemicals enter the organism.Faster thanThe rate at which organisms decompose and use it. This means that more chemicals enter than are discharged, leading to the accumulation of chemicals in organisms.
Another main way is that chemicals enter organisms, and organismsIt cannot be decomposed or excreted in some way.. So chemicals will continue to accumulate,Until it eventually becomes fatal to organisms..
All organismsThe problems we face are allThe result of dynamic balance between absorption and elimination. biological accumulationThe degree of occurrence determines the toxic effect.. In some cases, the protection mechanism is protected from certain undesirable substances deposited in special parts to prevent them.Participate in metabolic reaction.
The bioaccumulation description in this paper is used to evaluate the accumulation of drugs and their harmful metabolites in intestinal bacteria.
Therapeutic drugs will have a strong impact on intestinal microflora, and vice versa.Potential drug-bacterial interactions can be mediated by biologicalTransformation reduces microbial adaptability or changes drug availability.. The latter can have a positive or negative impact on drug activity and efficacy. Although drugs such as lovastatin and sulfasalazine will be chemically affected by intestinal bacteria.Convert into active formBut bacterial metabolism can make digoxin and so on.Drug inactivation, or like irinotecan (irinotecan).toxic effect. In order to further increase the diversity of susceptible drugs, it was recently reported that more than 100 molecules were chemically modified by intestinal bacteria.However, the mechanism of these interactions is mainly limited to drug biotransformation..
Lovastatin (lovastatin)
Lovastatin can reduce the synthesis of cholesterol and increase the synthesis of low-density lipoprotein receptor, mainly in the liver, resulting in the reduction of blood cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels, thus playing a role in the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease (source: Baidu Encyclopedia).
Sulfasalazine (sulfasalazine)
Sulfasalazine (sulfanilamide) is an antibacterial agent. It is a sulfonamide which is not easily absorbed by oral administration. The absorbed part is decomposed into 5-aminosalicylic acid and sulfapyridine under the action of intestinal microorganisms. 5-aminosalicylic acid stays in the intestinal wall tissue for a long time after complexing with the intestinal wall connective tissue, which plays an antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive role, such as reducing Escherichia coli and Clostridium, and inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandin and leukotrienes (source: Baidu Encyclopedia).
Digoxin
Digoxin is an intermediate cardiac glycoside, which is white crystal or crystalline powder. Odorless; It tastes bitter. In the treatment, the effect on the heart is positive inotropic effect, slowing down the heart rate and inhibiting heart conduction. It is suitable for congestive heart failure with low output, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
Bacteria in the intestine can regulate the availability and efficacy of therapeutic drugs. However, the potential mechanism of the interaction between drugs and bacteria is the chemical transformation or biological transformation of drugs by microorganisms.
A team of scientists from Heidelberg, Germany and Cambridge, England just published in Nature, and successfully studied the consumption of 15 drugs with different structures by 25 representative intestinal bacterial strains. 70 kinds of bacteria and drug interactions were revealed, 29 of which were not reported before. More than half of the new interactions can be attributed to biological accumulation.
This biological accumulation of intestinal bacteria may be a common mechanism to change drug availability and bacterial metabolism, which may have little effect on individuals.Biota composition, pharmacokinetics, side effects and drug reactionsHave an impact.
01
Drug non-metabolic accumulation
For a more detailed investigationDrugs and bacteriaA systematic map of the interaction between scientists.Two analytical methodsNuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) were used to systematically analyze 1.Five human targeted drugs and 25 human intestinal bacteria.Interaction between Bifidobacterium longum, Escherichia coli and other subspecies or strains of the same species of Bacteroides Homogeneous. Select bacterial species to cover those representing healthy microbial communities.Extensive phylogeny and metabolic diversity. In terms of drugs, 12 kinds of oral small molecular drugs (molecular weight less than 500 Da) were selected, which can be quantified based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography combined with ultraviolet detection (UPLC-UV) toCross different chemical, indication areas and side effects.
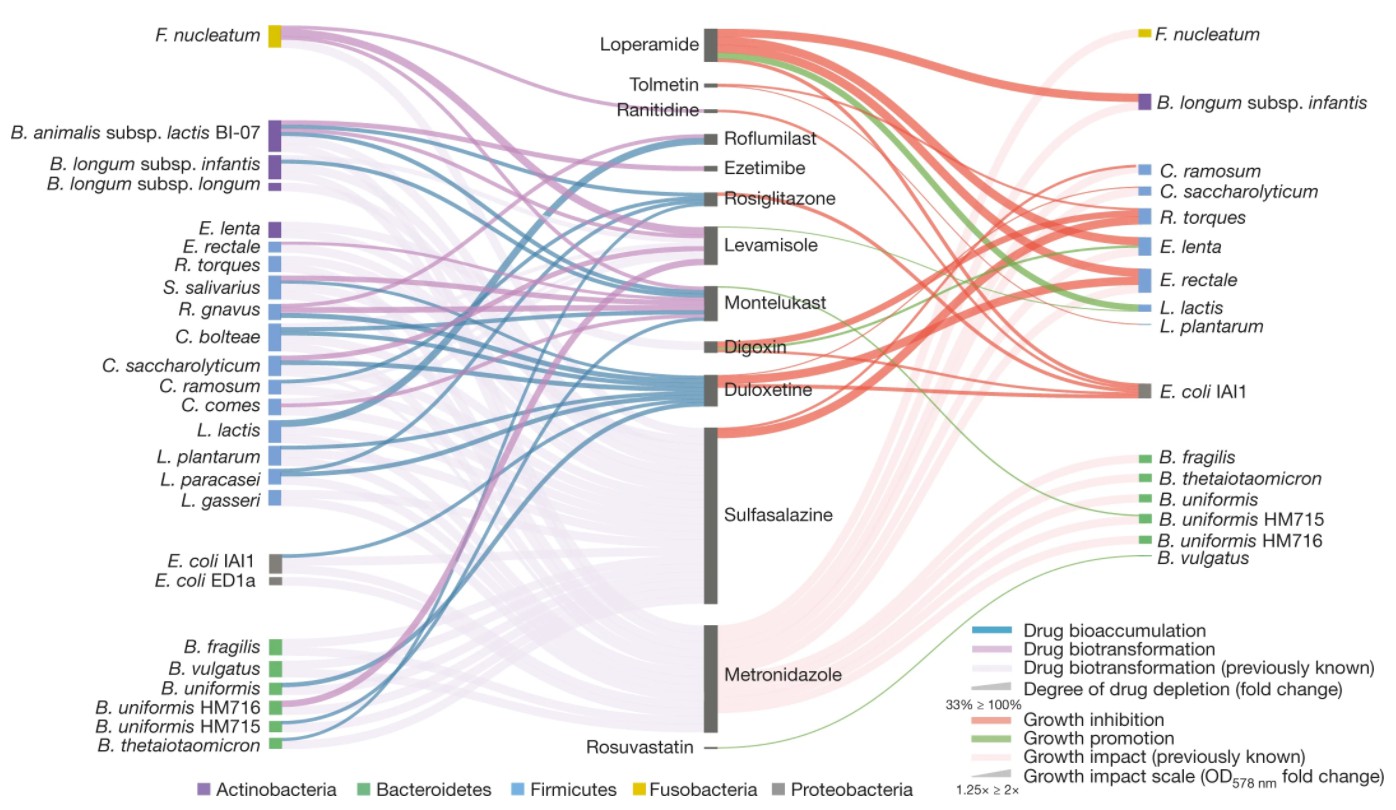
Bacterial-drug interaction network. Left network: biotransformation or accumulation of drugs by intestinal bacteria. Right network: the influence of drugs detected in at least two independent screening on the growth of intestinal bacteria (Student’s t test, α = 0.05). The full names of bacteria not mentioned in this paper are as follows: Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides vulgaris and Bifidobacterium animalis subspecies. Lactobacillus BI-07, Coprococcus come, Clostridium, Clostridium, lactobacillus paracasei, Ruminococcus gnavus.
Among the 29 newly discovered interactions (14 drugs and 4 drugs), as many as 17 species are bioaccumulation events.; That is to say,Drugs are stored by bacteria without changing it.. the rest Twelve interactions (8 drugs and 5 drugs) may represent biotransformation events.. Two of the five drugs: levamisole and ezetimibe, were indeedOther intestinal bacterial chemistry coursesDecorate.
Among bioaccumulative drugs,Antidepressant Duloxetine/Cymbalta(duloxetine) andRosiglitazone, a hypoglycemic drug.beThe only bioaccumulative drugEach species accumulates in many different species.
However, biodegradation and bioaccumulationInteraction is not mutually exclusive.. Montelukast (for asthma) and roflumilast (for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)Bioaccumulation by some bacteria and degradation by other bacteria.. In terms of bacteria, all strains except Fusobacterium nucleatum showed two types of interactions. In addition to the interaction with widely interacting control drugs sulfasalazine and metronidazole, the same strains of Bifidobacterium (B. uniformis) and Escherichia coli (E. coli) were found to be in the same strain.There is no overlap in interaction.. Because individuals usually have different strains, bioaccumulation is interactive.The prevalence rate may be higher than the research results..
Levamisole (levamisole)Levamisole is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic drug, which is mainly used to repel ascaris and hookworms. It can improve the resistance of patients to bacterial and viral infections. At present, it is used as adjuvant therapy for lung cancer and breast cancer after surgery or acute leukemia and malignant lymphoma after chemotherapy.
Ezetimibe (ezetimibe)Selective cholesterol absorption inhibitor is a lipid-lowering drug.
Duloxetine/Simpatine, mainly used to treat depression. It mainly regulates the balance of neurochemicals in brain tonic by inhibiting the recovery of serotonin and norepinephrine.
Rosiglitazone (rosiglitazone)Rosiglitazone and pioglitazone are thiazolidinedione hypoglycemic agents commonly used in clinical treatment in China at present. This product is an insulin sensitizer. By increasing the sensitivity of skeletal muscle, liver and adipose tissue to insulin and improving the utilization of glucose by cells, it can significantly reduce fasting blood glucose, insulin and C-peptide levels, and also reduce postprandial blood glucose and insulin. However, patients are required to have a certain ability to secrete insulin.
The World Health Organization’s International Agency for Research on Cancer listed rosiglitazone in the list of three carcinogens.
Due to manyHuman targeted drugs have been proved to affect the growth of intestinal bacteria.. The study examined the identifiedCan bacterial-drug interactions also lead to growth changes?. Although more than 30 major inhibitory drug-bacteria interactions have been detected, only.The three kinds of interactions involve both modifying growth and changing drug concentration.(excluding control drugs sulfasalazine and metronidazole). Therefore,The interaction between bacteria-drugs and drugs-bacteria seems to be largely independent..
In order to confirm the bioaccumulation of the interaction between bacteria and drugs, the study usedThe other two analytical methods are nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS).. As a case in point,Duloxetine, a widely used antidepressant, was found to be bioaccumulated by eight kinds of bacteria. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy can clearly detect duloxetine and confirm it.Four selected strains(Streptococcus salivarius, Bacteroides simplex, Escherichia coli IAI1 and Escherichia coli ED1a) were removed from the culture medium without biotransformation. LC-MS analysis in compound GMM medium also confirmed it.Clostridium saccharides and Escherichia coliBioaccumulation of IAI1 in the concentration range of 30 to 70.
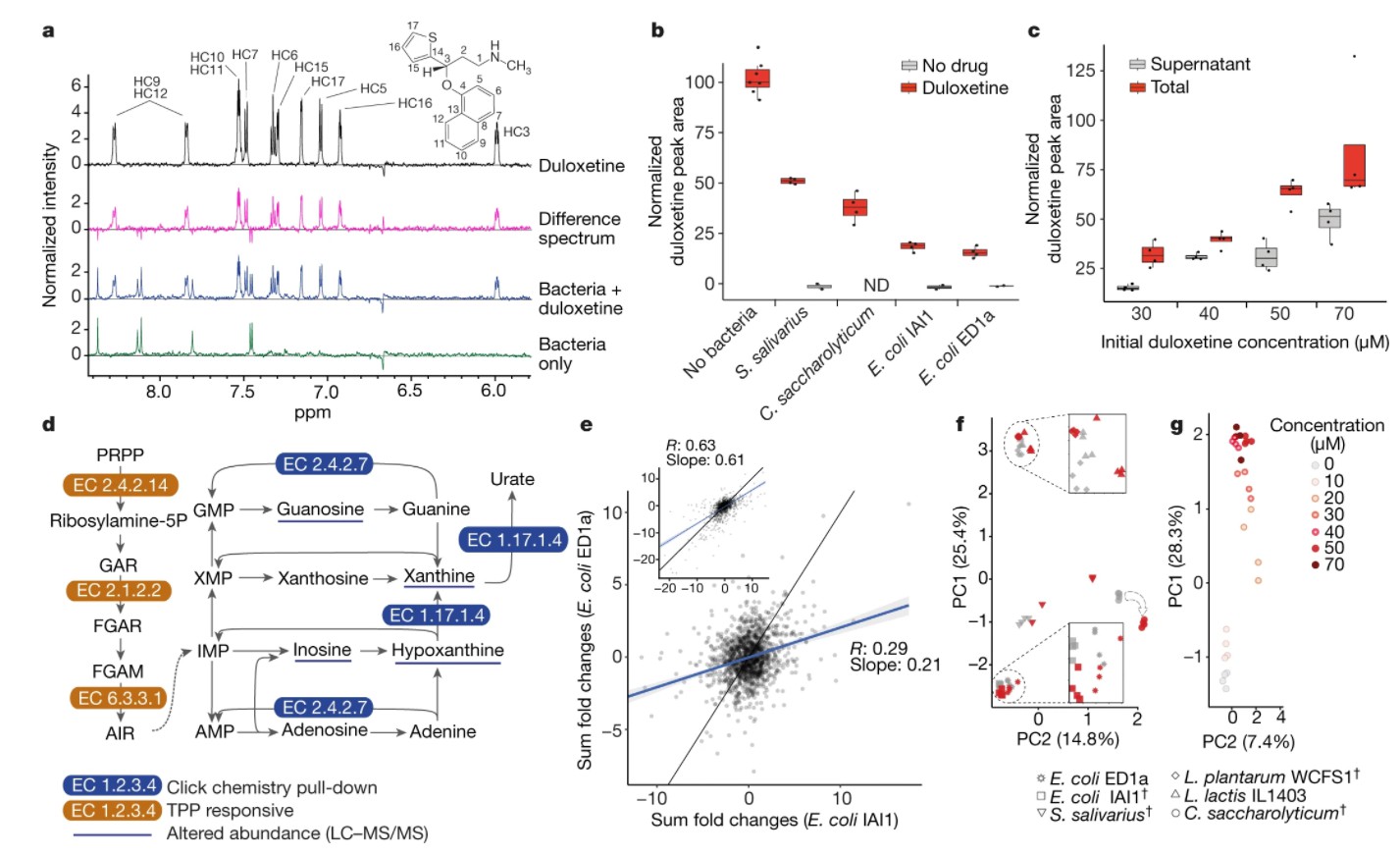
Nuclear magnetic resonance analysis showed that Streptococcus salivarius was sensitive to duloxetine.biotic pyramid
02
Biological accumulation affects cell metabolism.
Although biotransformation can be attributed tometabolic enzymeHowever, drug bioaccumulation is in mechanism.It’s even harder to imagine. In order to study the molecular basis of drug bioaccumulation by intestinal bacteria, scientists set out to determine the concentration of duloxetine in bioaccumulative strains.Protein target. Firstly, an acetylized, "clickable" molecular version was constructed and used as bait.
Click chemistry and thermal protein group analysis (TPP) showed that protein binding was a contributing factor to duloxetine bioaccumulation. This raises the question of whyThese two strains of E.coli showed different degrees of duloxetine bioaccumulation in GMM.. Two strains of Escherichia coli were compared in two different TPP assays, in which drugs were added to lysed cells or whole cells. Although TPP in cell lysate can find protein which is stable or unstable due to the direct binding of duloxetine, intact cell TPP can also capture the changes of cell reaction (changes of protein interaction and activity) in vivo.
Note: Click Chemistry, which aims to create various functional substances (candidate drug compounds, biological probes, soft materials, etc.), is a very widely used reaction. As a basic technology, it is characterized by high chemical selectivity, high yield, fast reaction speed and easy formation of strong chemical bonds.
In a complete cell assay,biotic pyramidThe IAI1 strain is more abundant than the abiotic ED1a strain.Has almost twice as muchDrug-reactive protein, and thermostable.The overall change is stronger. Consistent with the fact that duloxetine changed cell physiology more significantly in bioaccumulative strains, IAI1 strain also showed it in differentially expressed protein.A more obvious reaction.
In contrast, these two strains show very similar characteristics in TPP based on lysate, in which the lack of cell envelope enables drugs to reach all intracellular protein. Therefore,The strain specificity of bioaccumulation is probably due to the difference of absorption and consumption systems, which is similar to the transporter-dependent specificity observed in drug-drug interaction..
The combination of duloxetine and metabolic enzymes shows that the biological accumulatorMetabolism has changed.. To test this, two complementary metabolomics platforms were used-Flow injection analysis mass spectrometry (FIA-MS) and hydrophilic interaction chromatography combined with tandem mass spectrometry (HILIC-MS/MS).Methods: To analyze the effects of duloxetine treatment on six bacterial strains (four bioaccumulative and two non-bioaccumulative)Small molecule secretion.
Among the four strains, there are three bioaccumulative types (C. saccharolyticum, Lactobacillus plantarum and E.coli IAI1) and one non-bioaccumulative type (Lactococcus lactis), which show their characteristics after drug treatment in GMM.A significant shift in metabonomic patterns. The drug-induced changes in the ectometabolism group are equivalent to the interspecific differences.
In addition, the drug reaction was concentration-dependent, and no effect was observed on the non-bioaccumulated roflumilast. The concentration-dependent reaction to duloxetine was further verified by a subset of 71 metabolites, in which the chemical characteristics were presumed to be assigned-two metabolites confirmed by chemical standards-using tandem mass spectrometry. Clostridium saccharolyticum also showed a strong metabolic response to duloxetine when detected in nutrient-deficient PBS buffer.
Anyway,Protein omics and metabonomics data show that duloxetine binds to abundant metabolic enzymes to support its intracellular storage..
three
Biological accumulation leads to cross-feeding
Metabolic interaction is the basis of shaping the composition of intestinal microbial community.. So, will the metabolic changes related to biological accumulation affect the community composition?
In order to solve this problem, the researchers assembled five stable communities of intestinal bacterial species (Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, Eubacterium rectale, Lactobacillus gasseri, Ruminococcus bolts, Streptococcus salivarius) with and without duloxetine. One of these five species is S. salivarius, and the other is directly inhibited by E. rectale. These five species were co-inoculated in GMM and then transferred to fresh medium every 48 hours.
The existence of duloxetine significantly changed the community composition.Compared with the situation without drugs,The abundance of E.coli in rectum has increased by more than 100 times.. This is noteworthy because of the five species used by researchers,Rectal Escherichia coli is the most sensitive to duloxetine.. Consistent with Streptococcus salivarius as a bioaccumulator, duloxetine is exhausted in the supernatant of the community. Although decreasing the concentration of duloxetine can protect the rectal Escherichia coli in the community, it takes longer to reproduce in the presence of duloxetine.
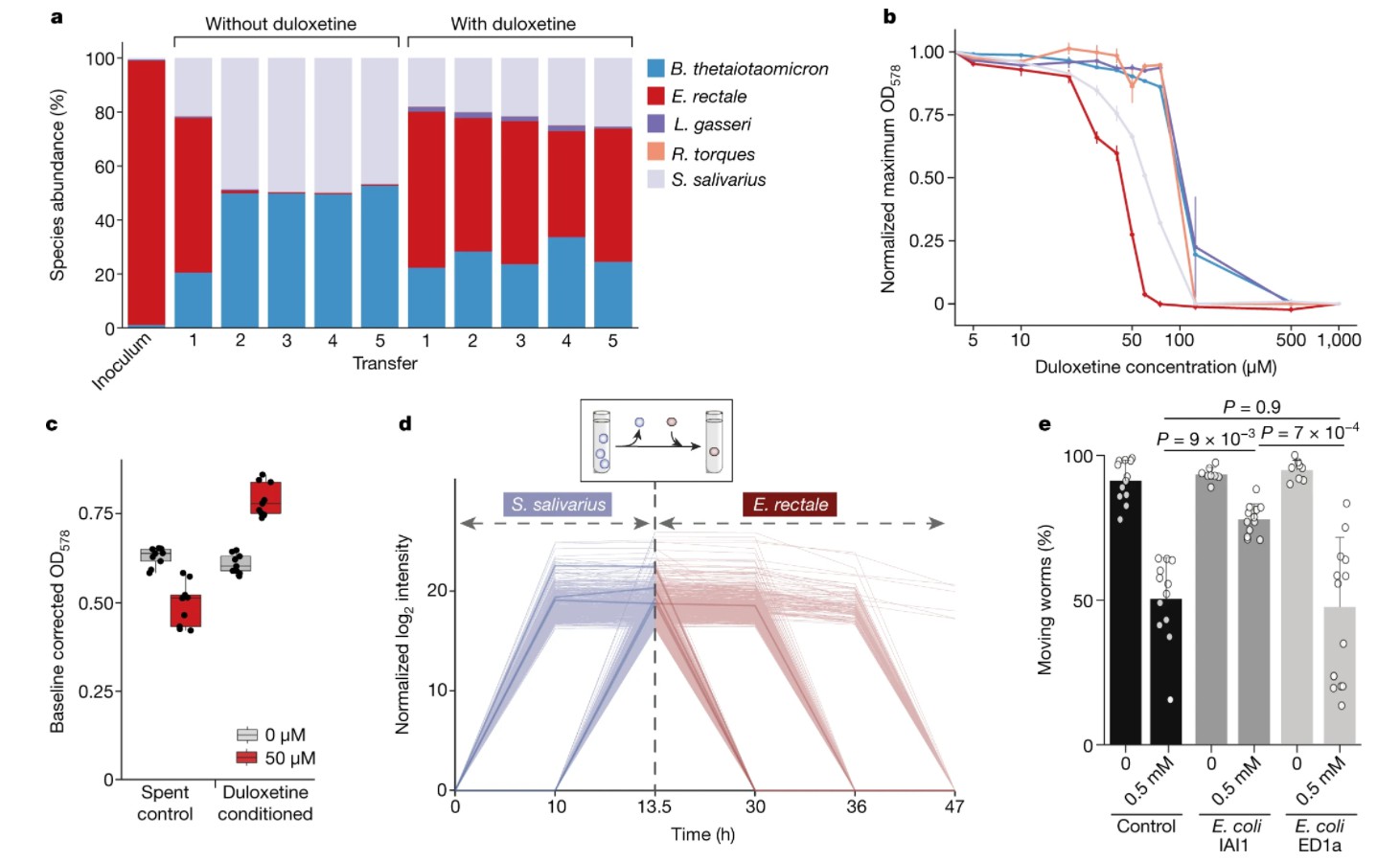
Duloxetine bioaccumulation changes community assembly and host response.
supposesalivaChanges in the secretion of duloxetine metabolites by Streptococcus liquidus can promote rectal Escherichia coli.. Supporting this, the used culture medium from S. salivarius grown in the presence of drugs improved the growth of E. rectale. Non-targeted metabolomics data from FIA-MS and HILIC-MS/MS further support the cross-feeding hypothesis.
Therefore, it was found that several metabolites were accumulated in the culture process of S. salivarius and then exhausted in the growth process of E. rectale. Among them, five metabolites are presumed to be annotated,Linolenic acid and cholic acidIt is confirmed by using analytical standards (methods). The changes of nucleotide-related metabolites (such as uridine -5′- diphosphate) are consistent with the critical nature of protein and metabolites influenced by duloxetine and E. rectale. Therefore,Human targeted drugs can regulate intestinal microbial community, not only by direct inhibition, but also by creating cross-feeding opportunities..
04
Bioaccumulation affects host response.
Then, the researchers used Caenorhabditis elegans as a model system to study the effect of duloxetine bioaccumulation on host response. Duloxetine as a kind ofSerotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitorAnd regulate the behavior (muscle movement) of Caenorhabditis elegans in a concentration-dependent manner.
In the presence of bioaccumulative species (Escherichia coli IAI1) as part of the growth medium of Caenorhabditis elegans, animal movements were examined as behavioral readings. As a closely related control, the researchers used E.coli ED1a strain which did not bioaccumulate in complex growth medium. In fact,Only strain IAI1, a bioaccumulation strain of duloxetine, weakened the influence of duloxetine on the host.Although the intestine of C. elegans is colonized by facultative anaerobic bacteria and obligate aerobic bacteria, it is likely to be aerobic, but the results are very consistent with the biological accumulation observed in anaerobic culture experiments.
Therefore, it is necessary to further study the microbiome-duloxetine-host interaction in other model systems or clinical environments.
05
Total knot
The results reveal that the therapeutic effect of host-targeted drugs can be achieved by intestinal bacteria in two ways.biotic pyramidTo adjust:
First, the main effect produced by reducing the availability of drugs;
Second, the secondary effect produced by changing the secretion of metabolites.
The latter willLead to changes in community composition.This is related to some drugsassistantAction and even the mode of action.. For the case drug duloxetine in this study, the intestinal bacterial interaction is indeed related to the side effects such as weight gain and its mode of action.
editorial comment/note
Bacteria in the intestine can affect the activity or efficacy of drugs. Recent studies show that this effect is not only biotransformation (changing the composition of drugs or metabolizing them into new substances),Bioaccumulation of drugs stored in cells by specific bacteriaIt may be another important influence (accounting for more than half of the newly discovered role). By accumulating drugs in cells, it willGreatly changes the efficacy of many dose-dependent drugs.(such as the antidepressant duloxetine under study), and it absorbs the bacteria that have accumulated drugs.Metabolism will change., which in turn willaffectInteracting with itOther bacteriaAnd finally change the composition of the flora.
References:
Klünemann M, Andrejev S, Blasche S, Mateus A, Phapale P, Devendran S, Vappiani J, Simon B, Scott TA, Kafkia E, Konstantinidis D, Zirngibl K, Mastrorilli E, Banzhaf M, Mackmull MT, H?velmann F, Nesme L, Brochado AR, Maier L, Bock T, Periwal V, Kumar M, Kim Y, Tramontano M, Schultz C, Beck M, Hennig J, Zimmermann M, Sévin DC, Cabreiro F, Savitski MM, Bork P, Typas A, Patil KR. Bioaccumulation of therapeutic drugs by human gut bacteria. Nature. 2021 Sep 8. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03891-8. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34497420.
关于作者