1905 movie network news …… There is a common name behind the classic masterpieces written in film history:.

French director luc besson is 64 years old, and his creativity is still amazing. He can write an average of 10 plays every year. The new film has achieved his personal breakthrough — — For the first time, it was shortlisted for the main competition unit of three major European film festivals. Luc besson is not only a successful commercial film director, but the recognition of the film festival once again confirms to the world audience that he is also a director with artistic and creative expression.
From the Venice International Film Festival to the Pingyao International Film Festival, and then to the China cinema, the douban score of "Dog God" soared from 7.1 points to the current 8.3 points, creating a "miracle" that triggered a sharp increase in word-of-mouth scores after its premiere. "Dog God" became luc besson’s highest score film on this platform after "This Killer is Not Too Cold", and also won the first high score in this year’s current Lunar New Year movie.

After the screening of Pingyao Film Festival, luc besson burst into tears in the face of cheers and applause from the audience. In an exclusive interview with 1905 Film Network, luc besson recalled this scene a few months ago. He said that while sitting in the first row and watching the film with everyone, he really felt the enthusiasm of the 1500 audience behind him. "After the film screening, everyone screamed and applauded, and the love and energy on my back made me cry."
So, how "God" is "Dog God"?

Dog God comes from a true story.
I was impressed by the leading actor’s acting skills and hoped that he would win an Oscar.
"I can’t understand how to abandon the child like this?"
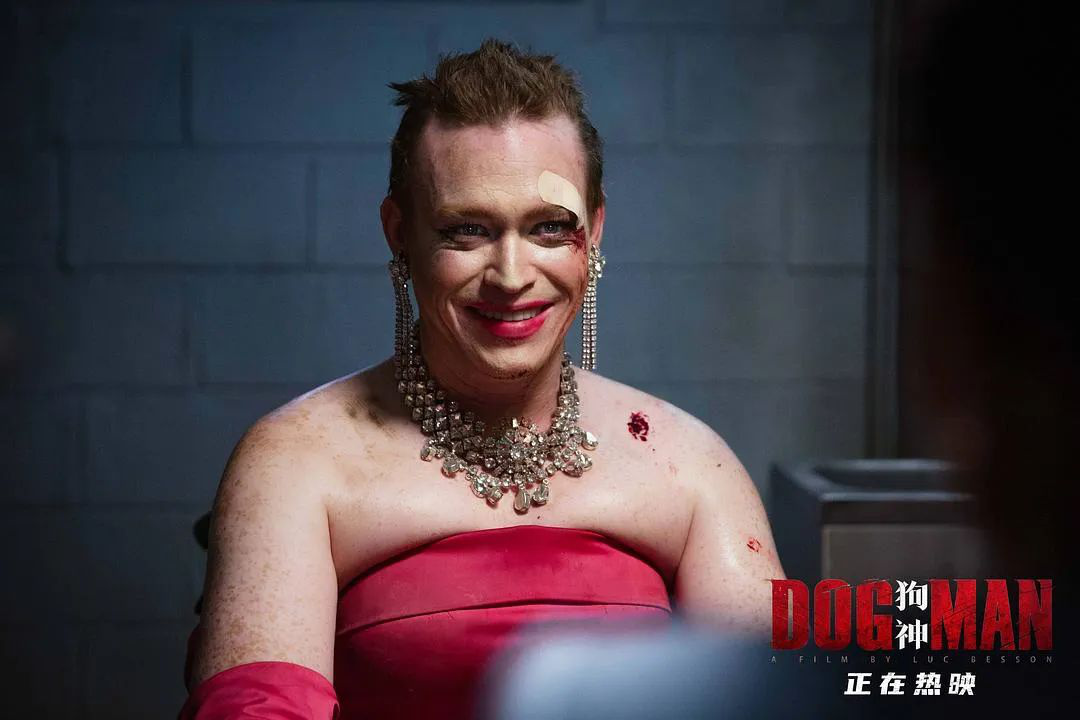
The God of Dogs is based on a true story, in which a father left his children in a cage for four years. As a father of five children, luc besson was shocked when he saw this report, which prompted him to write, starting with a father who threw his children into a dog cage.
"I tried to imagine what would happen when the child was 6 or 7 years old? What happens when you are 10 years old? What happens when you get out of the cage? What will happen at any time at the age of 20 or 25? Will he become a good person or a bad person? How does he face the pain? Will the pain be turned into a good thing or a bad thing? "

The core theme of the whole movie is "pain".
Douglas, the hero, is kind-hearted. Because he likes dogs, he is abused by his father who hates dogs and fights for a living. He lives in a dog cage and his legs are disabled by his father’s shotgun. His only companionship is the dogs around him, and he accidentally acquired the "super power" to communicate with them and give them action instructions, becoming the "dog god".
When he grew up, Douglas experienced a series of painful blows of love and survival. The stage performance art he loved was disillusioned with the marriage of the girl he admired, and the powerful forces of gangs also plagued him around, scarred both physically and mentally.
"No one can suffer more than him. He has suffered almost all the pains in the world, but he is still a good man," said luc besson, who wanted to convey this to the audience most.

Caleb landry jones, the Cannes-winning actress, has amazing acting skills, and her image has created the inner sensitivity and fragility of Douglas, the "Monroe killer", and her external courage and toughness.
Luc besson praised him, saying that he was one of the best actors he had ever worked with. "On a scale of 0 to 10, I will give him 25 points. The last time I saw such a talented actor was in "This killer is not too cold."
Sometimes, when watching Jones’ performance through the camera lens on the set, luc besson didn’t expect that the emotions he gave would be so rich. He thought that he would be exhausted after filming, but his emotions were still so calm, which impressed luc besson deeply.
"I haven’t seen a better actor this year!" Luc besson especially hopes that Jones can be shortlisted and win the Oscar for Best Actor with his superb performance in this film.

There are 120 dogs in the whole film, and the set is chaotic every day.
Scold the dog abuser: You should see a psychiatrist.
In the movie, Douglas has a group of well-trained and stunted "dog corps". He lives alone with the dogs, and the dogs comfort his wounds. They also cooperate tacitly and jointly fight against all those who have hurt him. He finally finds himself in the love of the dogs.
The crew specially recruited 120 dogs to form Douglas’s guard dog, covering every breed. The smallest is 1.5 kilograms, and the largest weighs 82 kilograms. It took four months to find and train them to live in harmony.
Among them, five dogs are star dogs with their own trainers. They undertake the performance functions similar to actors in the film and perform various action scenes, such as jumping into bed and stealing jewelry. More than 100 other dogs have not received any training.
"So it is chaotic, every day is a mess. Be patient to coordinate the chaos and pray for a miracle. It takes a lot of patience to shoot one shot at a time every day. " Luc besson said.

Luc besson likes dogs very much. He grew up with a dog named Socrates in his lonely childhood. Now they have a dog named Snoopy, which is 8 years old. I wanted to adopt the dog after the filming, but I gave up this idea considering that the arrival of the puppy might make the old Snoopy sad. Now he hopes Snoopy can live longer.
Luc besson is very angry about the dog abuse in society. "They should see a psychiatrist because dogs have unconditional love for us. Even if some dogs become fierce, it is because of human problems. All dogs are born kind like people. All those who beat animals just because they want to show their little power. "

It is often said in the film industry that the three most difficult elements to shoot are animals, children and water, and luc besson has filmed them all.
He has filmed Atlantis, Blue Sea and Blue Sky and other films about marine and underwater creatures. He directed the child star who made his first movie in The Killer Is Not Too Cold. After filming for 20 minutes on the first day of the boot, Natalie Portman wanted to go out and play.
One of the most difficult shots that luc besson experienced was to shoot devil fish and ask them to swim from the opposite side and then turn left. It was quite difficult to get six devil fish to do this continuous action instruction together, and finally it was made.
"When you are a director, you don’t care how hard it is. Sometimes it’s a dog, and sometimes it’s 11-year-old Natalie Portman. It’s not easy. You just do what you have to do. "

Some people say that I am a great director, but anyone can beat me.
Criticizing Hollywood and forgetting the original intention: just to make money and not to seek art
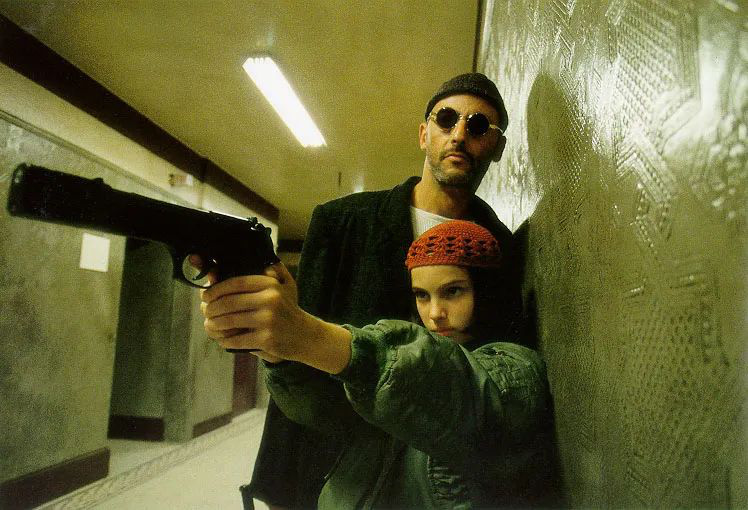
Since the first feature film "The Last Battle" was directed in 1983, luc besson has released too many classic films in his 40-year film career. The movie that is well-known in China and most loved by domestic audiences is "The Killer is not too cold".
On the TOP250 list of Douban movies, the film ranked fifth with 9.4 points. Looking at its rising ranking on the list in the past 30 years, luc besson is glad that a new generation of audiences will like this film, and it is expected to be introduced to China for the first time next year.

Luc besson said that he never wants to cater to the audience’s preferences. A movie usually takes two years to create from the start to the release. No one knows what the audience wants to see after two years, so he has to be honest with himself in creation. "Work with your brain and your heart and make the best movie you want to make."
Luc besson likes writing plays very much. He can write 10 plays every year. He thinks everyone is equal before creation. "Some people say that I am a great director, but anyone can beat me. No money or technology, just your hand and pen. "
His creative inspiration comes from real life, and I believe there is a story behind everyone. Although he is good at writing movies of action, crime, love, science fiction, adventure and comedy, he never considers the genre, but pays attention to the characters in his works and follows them to drive the development story. This is the case with Dog God.

When it comes to a series of superhero blockbusters that currently occupy the core market of Hollywood, luc besson is outspoken, criticizing that Hollywood has forgotten its original intention — — Follow artists, not money.
"Hollywood followed artists in the 1960s and 1980s. For example, a studio followed Scorsese and a studio followed Spielberg. Sometimes they can make good movies, sometimes they are not very good, but it doesn’t matter. If you don’t follow artists and only pursue figures and charts, you can’t make a good movie, which is impossible. It has been proved now that in a few years, Hollywood movies will go from bad to worse, and no one wants to watch them. They (the audience) will say that they are all the same rubbish. "
He strongly appealed to Hollywood: "Please return the power to the artist!"
Describe an old friend as a gentle "monster"
I look forward to exchanging new cooperation with China filmmakers.
Luc besson is an "old friend" of China’s films. In the past, there were many intersections and destinies with China’s films. He has made action films and movies tailored for Jet Li, and promoted the production of Sino-French co-productions and Star Agents: A City of Thousand Stars as a producer.
Talking about Jet Li, luc besson described it as follows: "As a soldier in the movie, he is a monster, but he is so gentle and polite. He can kill a person in 2 seconds without hurting a fly. "
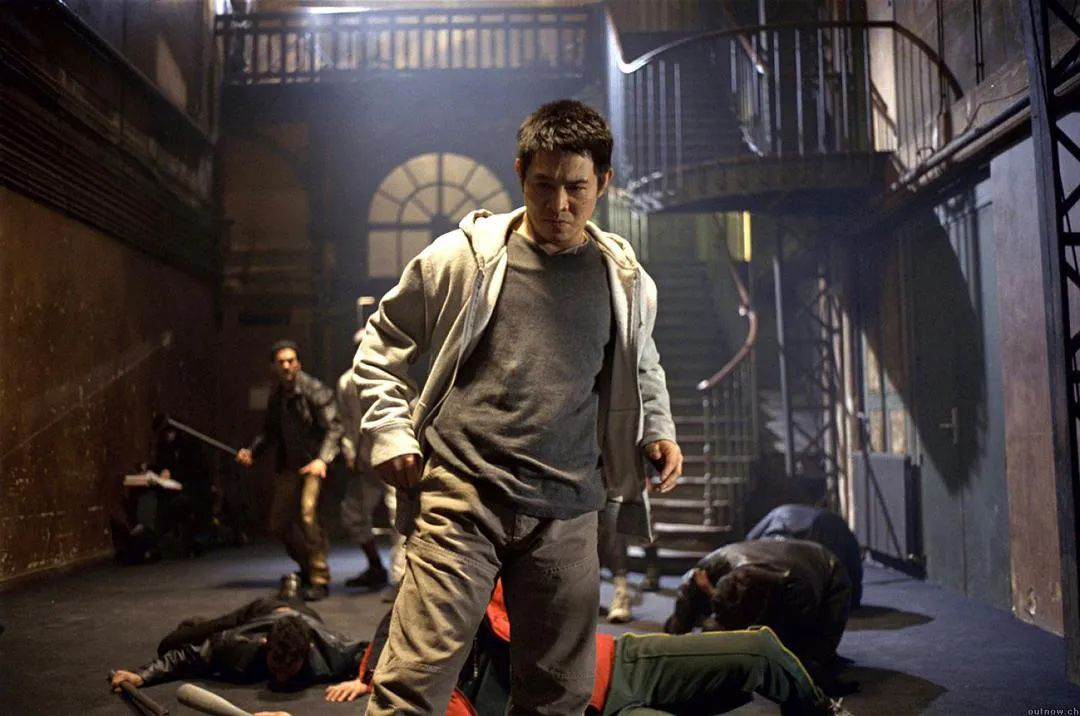

When they met for the first time in Paris, they hit it off and became friends. luc besson got inspiration from Jet Li and made movies together. They don’t consider the problem of China market or French market, but develop new movie stories from their meeting and collision.
For example, he took "God of Dogs" to Pingyao Film Festival, watched the director’s new film in Pingyao, had face-to-face communication with Ning Hao, and met many young filmmakers in China who were full of vitality in his heart. This trip to China made him feel very excited.
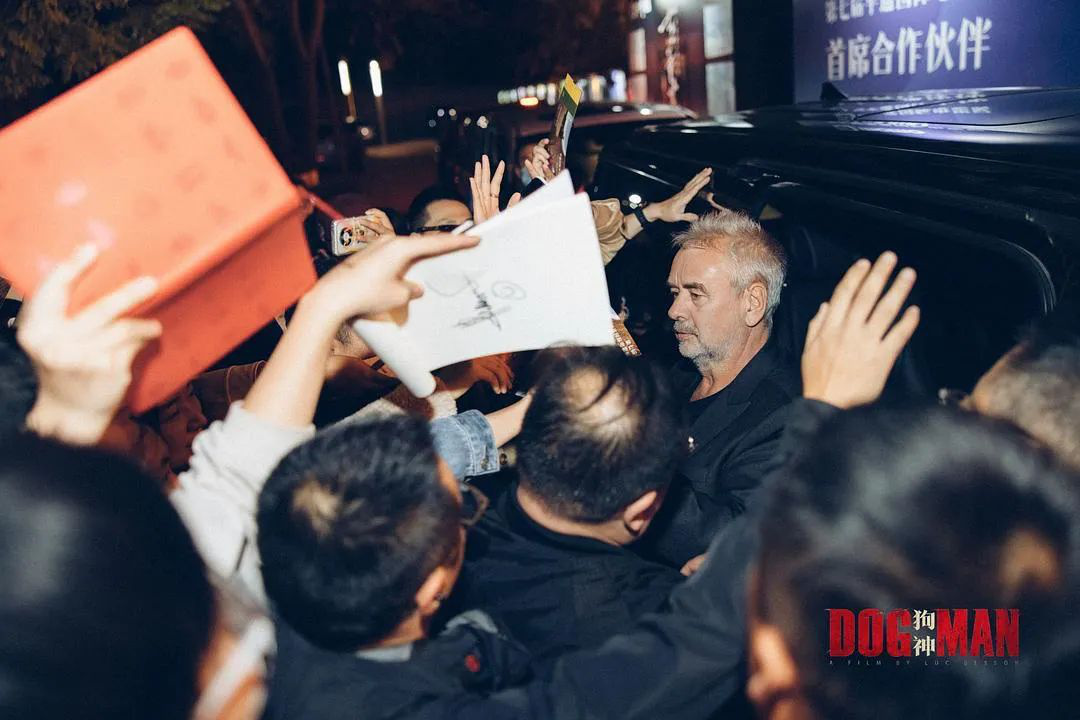

"China culture and French culture are so ancient and powerful that there are many similarities between the two cultures. We are always happy to meet and discuss. " Luc besson doesn’t know what movie he will cooperate with China next time. "There is no plan. My plan is to meet, communicate and absorb each other’s energy. "He believes that chatting will lead to new ideas and possibilities.